Federal Subsidies Climate Resilience: A Critical Review
Federal subsidies for climate resilience play a crucial role in shaping the future of vulnerable communities facing the dire impacts of climate change. By strategically withdrawing these financial incentives in high-risk areas, policymakers can discourage development in disaster-prone regions, thereby enhancing overall disaster resilience. This approach not only aids in protecting the environment through land conservation but also minimizes the financial burden on flood insurance systems. The linkage between climate change policies and federal support highlights the need for a comprehensive strategy that addresses the ongoing housing shortage while mitigating risks associated with natural disasters. As various studies illustrate, fostering a sustainable balance between development and environmental protection is essential for long-term community stability.
When examining the intersection of government financial aid and climate adaptability, it’s evident that federal subsidies for climate resilience are pivotal. These subsidies, essential for disaster preparedness and effective land management, can significantly influence urban planning in areas prone to extreme weather events. By prioritizing funding for projects that enhance sustainability and reduce exposure to climate risks, local governments can tackle issues like the housing crisis while promoting eco-friendly practices. Furthermore, integrating innovative climate change initiatives within urban development frameworks ensures that communities remain resilient against potential environmental threats. In essence, the strategic allocation of federal resources is fundamental to fostering a proactive approach to climate vulnerabilities.
The Impact of Federal Subsidies on Climate Resilience
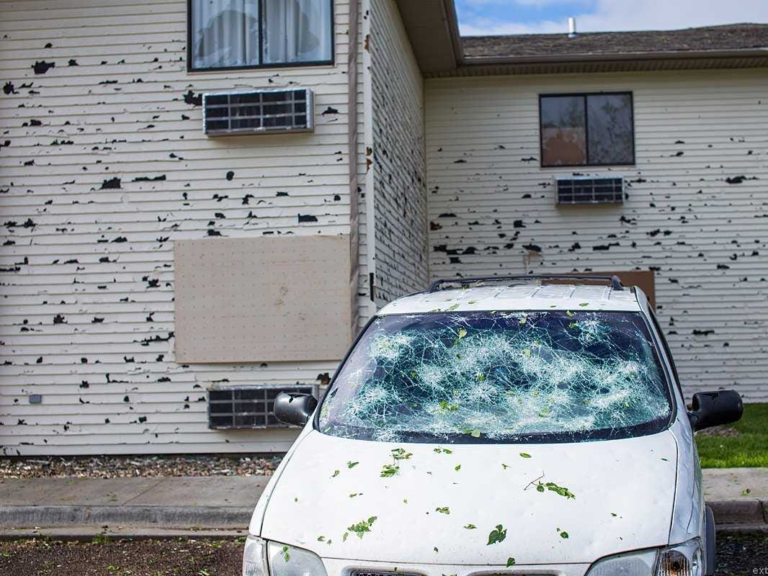
Federal subsidies play a crucial role in shaping climate resilience across various regions, particularly those vulnerable to disasters. The recent findings from the study published in Nature Climate Change indicate that withdrawing these subsidies in high-risk areas can discourage development. This approach not only protects the environment through land conservation but also promotes disaster resilience by reducing the number of structures prone to flood damage. By removing financial incentives for building in vulnerable locations, policymakers can help communities mitigate the impacts of climate change more effectively.
Moreover, the study notes that regions affected by the 1982 Coastal Barrier Resources Act (CBRA) demonstrate significant benefits from these policies. With fewer buildings per acre in CBRA-designated areas, the resulting natural infrastructure, such as wetlands, aids in flood mitigation. This underscores the importance of federal policies that align economic incentives with environmental sustainability, ensuring that communities can adapt to the challenges posed by climate change while also preserving critical ecosystems.
Disaster Resilience through Land Conservation Strategies
Land conservation emerges as a powerful strategy for enhancing disaster resilience, particularly in the face of increasing climate-related risks. Conserving natural landscapes not only serves to protect biodiversity but also functions as a crucial buffer against natural disasters. The recent research highlights how undeveloped wetlands, preserved through policies like the CBRA, provide essential services such as slowing floodwaters and absorbing excess rainfall, thus reducing the overall impact of floods on human settlements.
Additionally, integrating land conservation into local planning can yield long-term benefits for communities. By prioritizing the preservation of natural areas over development in high-risk zones, municipalities can create safer environments for their residents. This approach not only lessens the financial burdens associated with disaster recovery but also fosters sustainable growth, ensuring that housing projects are strategically placed away from flood-prone areas.
Navigating the Housing Shortage Amid Climate Challenges
As communities grapple with the dual challenges of a housing shortage and increasing natural disasters, the need for innovative solutions becomes increasingly urgent. The housing market’s pressure often leads to development in high-risk areas, which can exacerbate vulnerability to climate impacts. Policymakers must balance the need for affordable housing with the imperative to protect residents from disaster risks, ensuring that new developments are resilient and sustainable.
One potential solution lies in FEMA’s Community Rating System (CRS), which incentivizes improved floodplain management practices. By encouraging local governments to adopt measures that exceed the minimum standards, communities can both enhance their resilience to disasters and provide residents with significant reductions in flood insurance premiums. Ensuring more communities participate in the CRS can alleviate some of the housing shortages while simultaneously promoting safer living conditions for those at risk.
Innovative Flood Insurance Solutions for Climate Resilience
The landscape of flood insurance is undergoing significant changes, particularly in light of recent reforms aimed at making coverage more equitable and representative of actual risks. With the NFIP’s Risk Rating 2.0 reforms, property owners are now faced with premiums that reflect their specific flood risks, which has raised awareness about the importance of obtaining appropriate coverage. These changes highlight the necessity for homeowners, particularly those in areas prone to flooding, to understand their insurance needs and seek comprehensive protection.
In addition to traditional flood insurance, emerging strategies such as community-based catastrophe insurance and parametric insurance models present innovative ways to enhance financial protection against climate risks. These methods offer tailored solutions that can adapt to the unique challenges posed by climate change, ultimately promoting resilience in vulnerable communities. By fostering partnerships between public and private sectors, these innovative insurance solutions can help bridge the protection gap for residents living in high-risk areas.
The Role of Community Engagement in Climate Policy
Community engagement is vital in the formulation and implementation of climate policies, particularly those aimed at enhancing disaster resilience. Successful climate change policies are often those that actively involve local stakeholders in decision-making processes. By fostering dialogue between residents, local governments, and environmental organizations, communities can develop tailored strategies that address their unique vulnerabilities while ensuring that the needs of all stakeholders are met.
Moreover, effective public outreach and education campaigns can significantly improve understanding of climate risks and available resources. For instance, many homeowners remain unaware of their flood insurance options or the necessity of obtaining coverage beyond what is mandated by lenders. By enhancing public education on these matters, communities can empower residents to make informed decisions about their property, ultimately strengthening their resilience against climate-related disasters.
Public-Private Collaboration for Enhanced Resilience
Public-private collaboration is essential for addressing the complex challenges posed by climate change and fostering resilience in vulnerable communities. Such partnerships can leverage resources, expertise, and innovative solutions to tackle pressing issues like disaster management and housing shortages. By working together, government agencies and private sector stakeholders can create comprehensive strategies that not only meet immediate needs but also promote long-term sustainability.
For instance, initiatives that encourage investment in natural infrastructure, such as wetlands and green spaces, can provide multiple benefits, including flood mitigation and enhanced community well-being. These collaborations can also support the development of new insurance products that better reflect local risk profiles, ultimately ensuring that residents are protected against potential disasters while fostering economic growth.
Strategies for Effective Floodplain Management
Effective floodplain management is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change on vulnerable communities. By implementing comprehensive land use planning and zoning regulations, local governments can minimize the risks associated with flooding and promote disaster resilience. Prioritizing the preservation of floodplains and wetlands, for instance, can significantly reduce flood risks while maintaining important ecological functions.
Furthermore, adopting innovative floodplain management strategies, such as those promoted by FEMA’s Community Rating System, can provide communities with financial incentives to exceed minimum federal standards. These practices not only enhance safety and reduce potential damages from flooding but also contribute to the overall resilience of the community, ensuring that residents are better prepared for climate-related challenges.
Challenges in Educating Homeowners about Flood Insurance
Despite the critical importance of flood insurance, many homeowners remain unaware of their coverage options and the necessity of obtaining flood protection. This knowledge gap poses a significant risk, particularly in areas prone to flooding. Homeowners may mistakenly believe that their standard homeowners insurance covers flood damage, leaving them vulnerable to financial ruin following a disaster.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from the insurance industry, local governments, and community organizations to improve outreach and education. By providing clear information and resources about flood insurance options, communities can empower homeowners to make informed decisions and secure the necessary protection against climate impacts. This proactive approach can significantly enhance community resilience and reduce economic losses in the event of flooding.
Leveraging Natural Infrastructure for Flood Mitigation
Natural infrastructure, such as wetlands and forests, plays a vital role in flood mitigation and climate resilience. These ecosystems provide essential services, including floodwater absorption, sediment retention, and habitat preservation. By prioritizing the conservation of these natural areas, communities can enhance their resilience to climate-related disasters while also protecting biodiversity and promoting overall environmental health.
Investing in natural infrastructure not only helps mitigate flood risks but also offers economic benefits, such as reduced flood damages and lower insurance premiums. Policies that support land conservation and sustainable land-use practices can create a win-win situation, ensuring that communities are better prepared for climate change while also preserving valuable natural resources for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are federal subsidies for climate resilience and how do they relate to disaster resilience?
Federal subsidies for climate resilience refer to financial assistance programs aimed at enhancing the ability of communities to withstand and recover from climate-related disasters. These subsidies often support infrastructure improvements, land conservation efforts, and flood insurance initiatives, ultimately contributing to greater disaster resilience. By funding projects that mitigate climate risks, these subsidies help reduce the vulnerability of areas to adverse climate impacts.
How do federal subsidies impact land conservation efforts related to climate resilience?
Federal subsidies play a crucial role in land conservation efforts that promote climate resilience. By providing financial incentives for preserving natural ecosystems, these subsidies help maintain wetlands and forests, which naturally mitigate flood risks and enhance biodiversity. This conservation not only protects habitats but also contributes to the overall resilience of communities against climate change impacts.
Can federal subsidies help address the housing shortage while promoting climate resilience?
Yes, federal subsidies can help address the housing shortage while promoting climate resilience. By strategically directing funding towards resilient housing developments in safer areas, municipalities can increase affordable housing options without compromising disaster resilience. This approach requires a balance between meeting housing demands and ensuring that developments are not placed in high-risk flood zones.
What role do federal subsidies play in improving flood insurance accessibility?
Federal subsidies are essential for improving flood insurance accessibility, especially through programs like the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP). By encouraging participation in the Community Rating System (CRS), these subsidies provide discounts on flood insurance premiums for communities that implement effective floodplain management practices. This not only makes flood insurance more affordable but also promotes proactive disaster resilience.
How do climate change policies relate to federal subsidies for resilience?
Climate change policies often incorporate federal subsidies as a mechanism to support resilience efforts against climate-related risks. These policies aim to incentivize communities to adopt sustainable practices, invest in disaster preparedness, and enhance infrastructure resilience. By funding projects that align with climate change adaptation strategies, federal subsidies foster a proactive approach to mitigating the effects of climate change.
What are the long-term benefits of federal subsidies for climate resilience?
The long-term benefits of federal subsidies for climate resilience include reduced risk of disaster-related damages, lower flood insurance premiums, and enhanced community preparedness. By investing in resilience initiatives, communities can experience significant savings in recovery costs, improved public safety, and sustainable development that minimizes vulnerability to future climate impacts.
Why is public-private collaboration important in the context of federal subsidies for climate resilience?
Public-private collaboration is vital for maximizing the effectiveness of federal subsidies aimed at climate resilience. By fostering partnerships between government agencies and private sector stakeholders, resources can be pooled to develop innovative solutions for risk mitigation. This collaborative approach ensures that federal subsidies are utilized effectively, addressing the complexities of climate resilience and enhancing overall community preparedness.
How do federal subsidies affect the management of flood risks in vulnerable areas?
Federal subsidies significantly influence the management of flood risks in vulnerable areas by providing funding for infrastructure improvements and disaster preparedness initiatives. These subsidies encourage communities to implement robust flood management strategies, such as enhancing drainage systems and restoring natural barriers, which ultimately contribute to reduced flood risks and improved resilience against climate-related disasters.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Federal subsidies impact on development | Withdrawing federal subsidies in climate-vulnerable areas can deter development and promote disaster resilience. |
| Coastal Barrier Resources Act (CBRA) | The CBRA restricts incentives for development in high-risk areas, leading to fewer buildings and reduced flood damages. |
| Impact on neighboring areas | Undeveloped wetlands in restricted areas provide natural flood protection, benefiting adjacent zones. |
| Challenges with housing demand | Balancing the need for affordable housing with disaster resilience efforts requires coordinated local, state, and federal strategies. |
| Community Rating System (CRS) | FEMA’s CRS incentivizes better floodplain management, but only a small number of communities participate. |
| Public awareness of flood insurance | Many homeowners are unaware that flood coverage is not included in standard policies, increasing vulnerability. |
| Emerging risk mitigation strategies | Innovative methods like community-based catastrophe insurance and parametric insurance are being explored. |
Summary
Federal subsidies for climate resilience play a crucial role in shaping development patterns within climate-vulnerable areas. The recent study highlights that withdrawing such subsidies can effectively deter development in high-risk zones, promoting both disaster resilience and land conservation. By understanding the implications of federal incentives, communities can better coordinate their efforts to balance housing demands with the urgent need for climate risk mitigation.